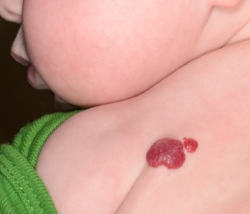
Hemangiomas are a type of vascular birthmark that appear right after birth or within the first few weeks of an infant’s life. They appear as bright red, purple, or pink papules or nodules that are soft to the touch and can occur on any part of the body. Some hemangiomas are quite persistent and stay on a child for a long period of time, while others fade away as a child grows. For the most part, these vascular growths are relatively benign except for in rare cases.
WHAT CAUSES HEMANGIOMAS?
The origin of hemangiomas is not fully known. It is suggested that they are caused by an unusual growth of blood vessels while a fetus is in utero. The unusual cluster and tangles of blood vessels can press upward into the skin, causing a hemangioma.
TREATING HEMANGIOMAS
Most hemangiomas do not need treatment, and close follow up and watchful waiting is all that is needed. These growths tend to disappear or reduce in size as a child grows. Other treatment options in persistent cases include oral and topical beta blockers, surgery, and laser treatment.